Introduction to GTIN
GTIN full form is Global Trade Item Number, a unique identifier for products used worldwide. GTINs are essential for the accurate identification and tracking of products in retail and supply chain operations.
Importance of GTIN in Retail
The Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) is crucial for ensuring products are correctly identified across various platforms and locations, facilitating smooth transactions and inventory management. Its adoption has revolutionized the retail industry by standardizing product identification globally. gtin full form stands for Global Trade Item Number, was introduced to provide a global standard for product identification, replacing multiple incompatible systems. Over time, it has become the cornerstone of retail product identification, supported by organizations like GS1, which oversees its implementation and updates.
GTIN Components Explained
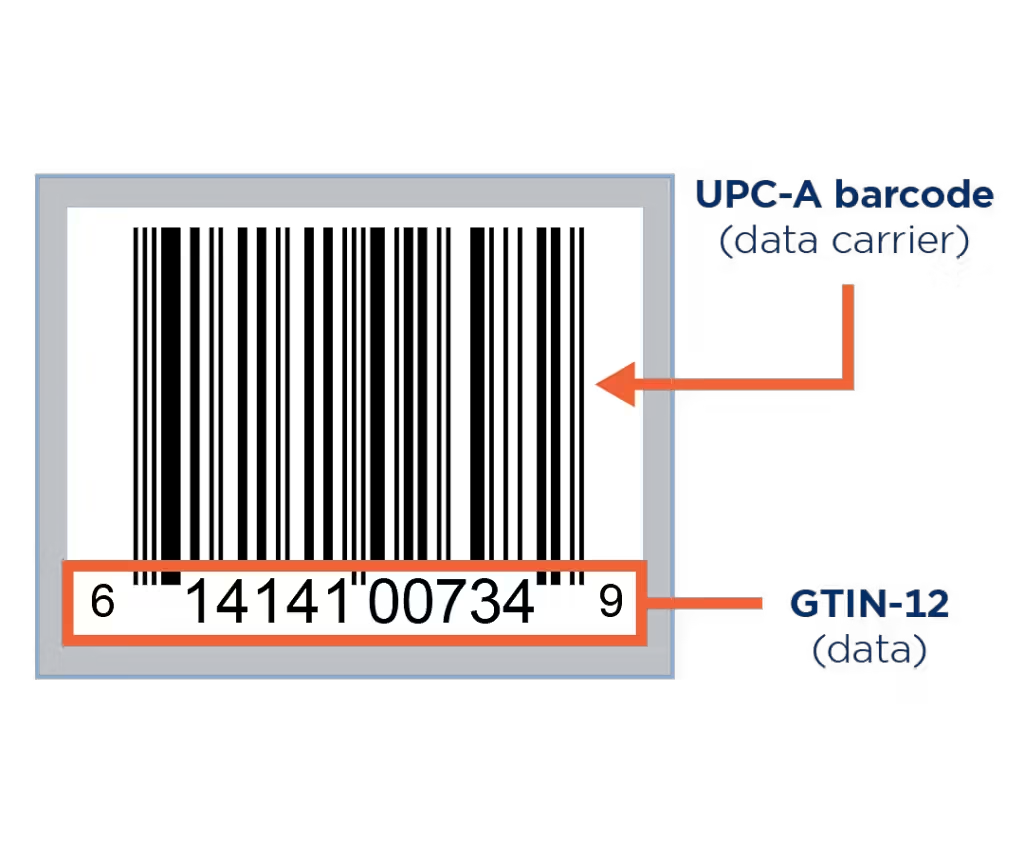
GTIN-8, GTIN-12, GTIN-13, and GTIN-14
GTINs come in several formats, including GTIN-8, GTIN-12, GTIN-13, and GTIN-14, each serving different types of products and packaging:
- GTIN-8: Used for small items and typically found on smaller packages.
- GTIN-12: Commonly known as the Universal Product Code (UPC) in North America.
- GTIN-13: Known as the European Article Number (EAN), widely used outside North America.
- GTIN-14: Used for grouping products at different packaging levels.
Breakdown of Each Component
Each GTIN is composed of a company prefix, item reference, and a check digit. The company prefix identifies the manufacturer, the item reference identifies the specific product, and the check digit ensures the code’s accuracy.
Differences Between GTINs and UPCs
While GTIN-12 is synonymous with the UPC, GTINs encompass a broader range of codes, including GTIN-13 (EAN) and GTIN-14, making them more versatile for global trade.
Benefits of GTIN in Retail
Improved Inventory Management
GTINs allow for precise inventory tracking, reducing errors and ensuring that stock levels are accurately monitored. This leads to better inventory control and reduced out-of-stock situations.
Streamlined Supply Chain Operations
With standardized product identification, GTINs facilitate smoother supply chain operations, from manufacturing to distribution. This standardization helps reduce bottlenecks and improves overall efficiency.
Enhanced Product Traceability
GTINs improve product traceability, enabling retailers to track products through the supply chain, ensuring quality control, and swiftly addressing any issues such as recalls.
Better Customer Experience
Accurate product identification and enhanced traceability improve the customer experience by ensuring product availability and authenticity, building consumer trust.
GTIN Implementation in Retail
Retailers and manufacturers must assign a unique GTIN to each product variant. This involves obtaining a company prefix from GS1 and following guidelines for item reference and check digit calculations. GTINs must be integrated with barcode systems to enable scanning and tracking. This integration ensures seamless operations across the supply chain and at the point of sale. Best practices for using GTINs include maintaining accurate product information, regularly updating records, and ensuring all products are correctly labeled with their respective GTINs.
GTIN’s Role in E-commerce
In e-commerce, GTINs play a vital role in product listings and search visibility. They help online marketplaces standardize listings, making it easier for customers to find and compare products.
Products with GTINs are more likely to appear in search results, improving their visibility and increasing sales opportunities. Accurate GTINs also enhance the quality of product listings by providing consistent and reliable information.
Online marketplaces like Amazon and eBay require sellers to provide GTINs for their products. Compliance with these requirements is crucial for listing products and avoiding potential penalties.
Challenges and Solutions with GTIN Adoption
Data Accuracy and Integrity
Maintaining accurate GTIN data is essential. Retailers must implement robust data management practices to ensure the integrity of product information.
GTIN Standardization Across Different Regions
Standardizing GTIN use across different regions can be challenging due to varying regulations. Working with GS1, which is the only authorized organization to issue the 890 barcode prefix in India, helps ensure compliance and consistency.
Addressing Counterfeit and Duplicate GTINs
To combat counterfeit and duplicate GTINs, retailers should use GS1’s verification services and maintain strict control over their GTIN allocations.
Future Trends of GTIN in Retail
Advancements in GTIN technology, including integration with digital platforms and enhanced data capabilities, will further streamline product identification and tracking.
The integration of GTINs with RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and IoT (Internet of Things) will enhance real-time tracking and data collection, improving supply chain visibility and efficiency. These technological advancements will lead to more efficient retail operations and enhanced customer experiences, providing retailers with more tools to meet consumer demands.
Key Takeaways and Lessons Learned from Case Studies
The key takeaways from these case studies include the importance of accurate data management, the benefits of standardized product identification, and the need for ongoing collaboration with GS1.
Conclusion
GTINs are essential for accurate product identification, efficient supply chain operations, and enhanced customer experiences in retail. The benefits of GTINs include improved inventory management, streamlined supply chain operations, and better product traceability. Challenges include ensuring data accuracy and combating counterfeiting, while future trends point towards greater integration with emerging technologies.
Retailers should prioritize GTIN adoption to stay competitive and meet consumer expectations. By subscribing with GS1 India, the only authorized organization to issue the 890 barcode prefix in India, retailers can ensure compliance and leverage the full benefits of GTINs.